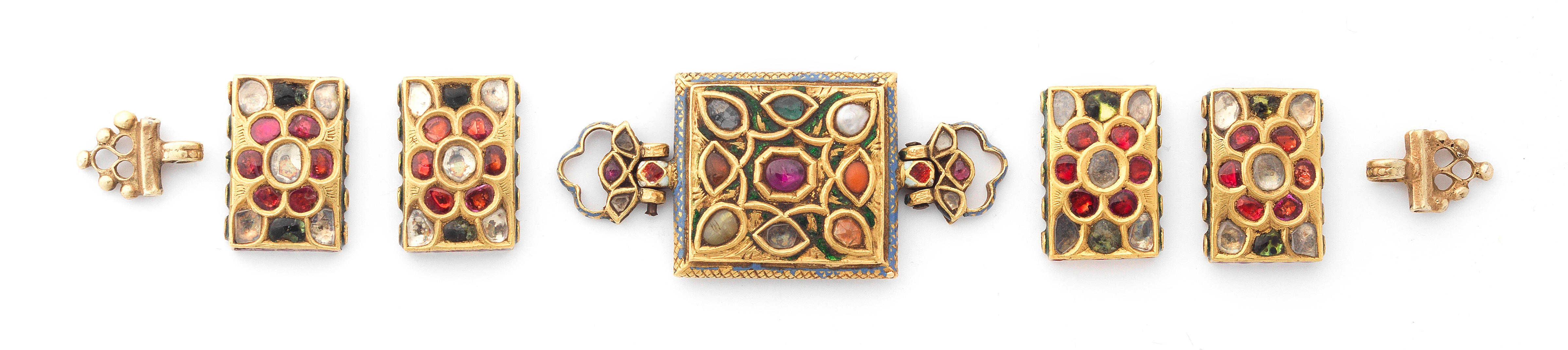
A gem-set enamelled gold armlet from the collection of Maharani Jindan Kaur (1817-63), wife of Maharajah Ranjit Singh (1780-1839)
Punjab, probably Lahore, first half of the 19th Centurycomprising eleven rectangular elements each set with a central gem in gold kundan, including a diamond, a garnet, a turquoise, a cats eye chrysoberyl, a pearl and coral (corallium rubrum), on a ground of polychrome enamel, the reverse decorated in polychrome enamel with floral motifs, with loop and ball fastening
15.5 cm. long excluding fastening; 38.3 g.FootnotesProvenance
Maharani Jindan Kaur (1817-63), wife of Maharajah Ranjit Singh (1780-1839).
Princess Sophia Alexandrovna Duleep Singh (1876–1948), gifted by her father HH Maharajah Duleep Singh, later given by the Princess to her life-long personal companion and employee Mrs Ivy Janet Lane.
Mrs Dora Crowe of Hampton House, Blo' Norton, acquired from Mrs Ivy Janet Lane.
Private UK collection, acquired from Mrs. Oriel Sutherland, daughter of Mrs. Dora Crowe.
Published
Peter Bance, Sovereign, Squire and Rebel: Maharajah Duleep Singh and the Heirs of a Lost Kingdom, London, 2009, p. 53, no. 53.
Exhibited
Maharajah Duleep Singh Exhibition, Museum of Thetford Life, Thetford, Norfolk, 19 June 2010 - 11 June 2011.
Featured in the Digital 3D Exhibition by the Sikh Museum Initiative, Leicester, 2019.
Dora Crowe was head housekeeper and companion to Princess Bamba Sutherland at Hampton House, Blo Norton. Her husband Cyril, who was formerly in the service of Prince Frederick Duleep Singh, later became caretaker at Hampton House. For more details on the Crowe family, see Sovereign, Squire & Rebel (Coronet House, 2000), p. 260.
Mrs Ivy Janet Lane and her husband John were both in the service of Princess Sophia Duleep Singh at Faraday House for many years as companions and housekeepers to the Princess.
This armlet was likely to have been within the casket of jewels handed back to Maharani Jindan Kaur (1817-1863) by the British authorities when she agreed to live in London with her son, who she was reunited with in Calcutta in 1861. Duleep Singh had not only negotiated a £3,000-a-year pension for his mother but also the safe return of over 600 pieces of her personal jewellery that had been impounded by the British authorities at Benares when she fled to Nepal. In the UK, John Login expedited the passage of her jewels through customs and Lady Login was present when Jind Kaur was finally reunited with them in London: 'Her jewels had at the moment arrived from the Custom House, and so delighted was she at the sight, that she forthwith decorated herself, and her attendants, with an assortment of the most wonderful necklaces and earrings, strings of lovely pearls and emeralds being arranged, in graceful concession to English fashion...' (Lady Lena Campbell Login, John Login and Duleep Singh, London 1890, p 213).
These important personal royal effects of the late Maharani were dispersed after her death by her son and grandchildren, either through auction salerooms or by being gifted away. Two decades after her death, when Maharaja Duleep Singh lost his battle against the India Office over the thorny issue of his financial allowances, he decided to auction off some of his possessions in order to raise £20,000 with a view to relocating to India where he could live as a person of importance. He stripped his stately home at Elveden of some choice valuables – including 25,000 ounces of chased silver gilt, rare Indian carpets, Indian shawls, embroideries and a casket of jewels (though 'no old family jewels' according to the press, The Gentleman's Magazine and Historical Review, London, September 1863, p 378) – and packed them up to be auctioned by Messrs Phillips, Son & Neale of New Bond Street. A sympathetic editorial in The Times (20 July 1883) noted how 'news of His Highness being compelled to sell his jewels and other valuables will excite a deep feeling of sympathy among all who are acquainted with the history of the "Lion of the Punjab".' The following year, his embittered relations with the British Government compelled him be ransack the contents of Elveden to provide the finances needed to resettle in Punjab with his family. From 27 April to 5 May 1886, while the Maharaja was detained at Aden as he attempted to gain onward passage to India, the auction only realised a fraction of the expected value of the items, forcing Duleep Singh to empty his Coutts safety-deposit box of all his most valuable jewels. When he failed to gain the support of the Russians, Duleep Singh decided to settle in Paris. In 1890, he was forced to sell what remained of the family jewels in his possession to pay for both his own accommodation and that of his estranged second wife, Ada, who moved into an expensive villa situated in an exclusive tree-lined suburb of Paris.
Prince Victor Duleep Singh, the maharaja's eldest son, sold part of his inheritance in order to pay off his considerable debts. On 19 June 1899, Messrs Christie Manson & Woods sold 114 lots from Victor's collection in their London sales room including Indian gold jewellery 'formerly the property of the late Maharajahs Duleep Singh and Runjeet Singh of Lahore' according to The Daily Telegraph (20 June 1899, p. 9). Of the riches snapped up at the well-attended auction, which realised nearly £3,000, The Morning Post gave the following details of the best prices achieved, including a lavish horse's head ornament: a gold forehead ornament with diamonds, and ruby drops, from Dholepore, £35; a breast ornament of gold, set with stones and pearls, from Kangra, £46; pair of forehead ornaments, of crescent form, from Delhi, £41; pair of gold armlets, Lucknow, £35; a gold girdle centre set with stones, Delhi, £44; a large ornament for horse's head, of gold, enamelled, from Punjaub, and part of the State harness of Runjeet Singh, £44;... a massive gold horse frontlet, thickly studded with emeralds and rubies, Delhi, £210.... (The Morning Post, 20 June 1899, p 3).
In 1897, Princess Bamba and her two sisters, Princesses Sophia and Catherine, moved to the Norfolk village of Old Buckenham, where they lived near another brother, Prince Frederick. When he sold his house in 1906 and shifted to Blo' Norton, his sisters followed suit. In 1935, the princesses shifted from Blo' Norton Hall to Hampton House at Blo' Norton. When the lease came to an end in 1935, Princess Sophia installed a married couple Dora and Cyril Crowe (Cyril had been a childhood-friend of Frederick's), with their baby son Cyril Junior, at Hampton House to attend upon the princesses whenever they stayed there. When Sophia died in 1948, Bamba became the last surviving member of Duleep Singh's family from his first marriage. Bamba took up residence at Hilden Hall as well as the management of Hampton House. Her relationship with the Crowes developed in terms of mutual respect and affection. While Cyril Jr had been a great favourite with Sophia, his sister Oriel, who was eight years younger, was much loved by Bamba. In later life, the young girl would recall how 'Princess Bamba retained her sense of humour, and as an old lady she would smile, wrinkle her nose, and giggle like a little girl' (Peter Bance, Sovereign, Squire and Rebel: Maharajah Duleep Singh, London 2009, p 160).
In 1953, Bamba decided to give Hampton House to the Crowes as she planned to return to Lahore (she had visited Punjab's capital in 1941 but was forced to remain there for five years following the outbreak of the Second World War). She died in her family's ancestral home in 1957. According to Oriel Crowe's (later Sutherland) letter of provenance accompanying this lot, Princess Sophia gifted the armlet to Mrs Ivy Janet, who later gave it to her. A forehead ornament with the same provenance was sold at Bonhams, Islamic and Indian Art, 11 June 2020, lot 230.
A gem-set enamelled gold armlet from the collection of Maharani Jindan Kaur (1817-63), wife of Maharajah Ranjit Singh (1780-1839)
Punjab, probably Lahore, first half of the 19th Centurycomprising eleven rectangular elements each set with a central gem in gold kundan, including a diamond, a garnet, a turquoise, a cats eye chrysoberyl, a pearl and coral (corallium rubrum), on a ground of polychrome enamel, the reverse decorated in polychrome enamel with floral motifs, with loop and ball fastening
15.5 cm. long excluding fastening; 38.3 g.FootnotesProvenance
Maharani Jindan Kaur (1817-63), wife of Maharajah Ranjit Singh (1780-1839).
Princess Sophia Alexandrovna Duleep Singh (1876–1948), gifted by her father HH Maharajah Duleep Singh, later given by the Princess to her life-long personal companion and employee Mrs Ivy Janet Lane.
Mrs Dora Crowe of Hampton House, Blo' Norton, acquired from Mrs Ivy Janet Lane.
Private UK collection, acquired from Mrs. Oriel Sutherland, daughter of Mrs. Dora Crowe.
Published
Peter Bance, Sovereign, Squire and Rebel: Maharajah Duleep Singh and the Heirs of a Lost Kingdom, London, 2009, p. 53, no. 53.
Exhibited
Maharajah Duleep Singh Exhibition, Museum of Thetford Life, Thetford, Norfolk, 19 June 2010 - 11 June 2011.
Featured in the Digital 3D Exhibition by the Sikh Museum Initiative, Leicester, 2019.
Dora Crowe was head housekeeper and companion to Princess Bamba Sutherland at Hampton House, Blo Norton. Her husband Cyril, who was formerly in the service of Prince Frederick Duleep Singh, later became caretaker at Hampton House. For more details on the Crowe family, see Sovereign, Squire & Rebel (Coronet House, 2000), p. 260.
Mrs Ivy Janet Lane and her husband John were both in the service of Princess Sophia Duleep Singh at Faraday House for many years as companions and housekeepers to the Princess.
This armlet was likely to have been within the casket of jewels handed back to Maharani Jindan Kaur (1817-1863) by the British authorities when she agreed to live in London with her son, who she was reunited with in Calcutta in 1861. Duleep Singh had not only negotiated a £3,000-a-year pension for his mother but also the safe return of over 600 pieces of her personal jewellery that had been impounded by the British authorities at Benares when she fled to Nepal. In the UK, John Login expedited the passage of her jewels through customs and Lady Login was present when Jind Kaur was finally reunited with them in London: 'Her jewels had at the moment arrived from the Custom House, and so delighted was she at the sight, that she forthwith decorated herself, and her attendants, with an assortment of the most wonderful necklaces and earrings, strings of lovely pearls and emeralds being arranged, in graceful concession to English fashion...' (Lady Lena Campbell Login, John Login and Duleep Singh, London 1890, p 213).
These important personal royal effects of the late Maharani were dispersed after her death by her son and grandchildren, either through auction salerooms or by being gifted away. Two decades after her death, when Maharaja Duleep Singh lost his battle against the India Office over the thorny issue of his financial allowances, he decided to auction off some of his possessions in order to raise £20,000 with a view to relocating to India where he could live as a person of importance. He stripped his stately home at Elveden of some choice valuables – including 25,000 ounces of chased silver gilt, rare Indian carpets, Indian shawls, embroideries and a casket of jewels (though 'no old family jewels' according to the press, The Gentleman's Magazine and Historical Review, London, September 1863, p 378) – and packed them up to be auctioned by Messrs Phillips, Son & Neale of New Bond Street. A sympathetic editorial in The Times (20 July 1883) noted how 'news of His Highness being compelled to sell his jewels and other valuables will excite a deep feeling of sympathy among all who are acquainted with the history of the "Lion of the Punjab".' The following year, his embittered relations with the British Government compelled him be ransack the contents of Elveden to provide the finances needed to resettle in Punjab with his family. From 27 April to 5 May 1886, while the Maharaja was detained at Aden as he attempted to gain onward passage to India, the auction only realised a fraction of the expected value of the items, forcing Duleep Singh to empty his Coutts safety-deposit box of all his most valuable jewels. When he failed to gain the support of the Russians, Duleep Singh decided to settle in Paris. In 1890, he was forced to sell what remained of the family jewels in his possession to pay for both his own accommodation and that of his estranged second wife, Ada, who moved into an expensive villa situated in an exclusive tree-lined suburb of Paris.
Prince Victor Duleep Singh, the maharaja's eldest son, sold part of his inheritance in order to pay off his considerable debts. On 19 June 1899, Messrs Christie Manson & Woods sold 114 lots from Victor's collection in their London sales room including Indian gold jewellery 'formerly the property of the late Maharajahs Duleep Singh and Runjeet Singh of Lahore' according to The Daily Telegraph (20 June 1899, p. 9). Of the riches snapped up at the well-attended auction, which realised nearly £3,000, The Morning Post gave the following details of the best prices achieved, including a lavish horse's head ornament: a gold forehead ornament with diamonds, and ruby drops, from Dholepore, £35; a breast ornament of gold, set with stones and pearls, from Kangra, £46; pair of forehead ornaments, of crescent form, from Delhi, £41; pair of gold armlets, Lucknow, £35; a gold girdle centre set with stones, Delhi, £44; a large ornament for horse's head, of gold, enamelled, from Punjaub, and part of the State harness of Runjeet Singh, £44;... a massive gold horse frontlet, thickly studded with emeralds and rubies, Delhi, £210.... (The Morning Post, 20 June 1899, p 3).
In 1897, Princess Bamba and her two sisters, Princesses Sophia and Catherine, moved to the Norfolk village of Old Buckenham, where they lived near another brother, Prince Frederick. When he sold his house in 1906 and shifted to Blo' Norton, his sisters followed suit. In 1935, the princesses shifted from Blo' Norton Hall to Hampton House at Blo' Norton. When the lease came to an end in 1935, Princess Sophia installed a married couple Dora and Cyril Crowe (Cyril had been a childhood-friend of Frederick's), with their baby son Cyril Junior, at Hampton House to attend upon the princesses whenever they stayed there. When Sophia died in 1948, Bamba became the last surviving member of Duleep Singh's family from his first marriage. Bamba took up residence at Hilden Hall as well as the management of Hampton House. Her relationship with the Crowes developed in terms of mutual respect and affection. While Cyril Jr had been a great favourite with Sophia, his sister Oriel, who was eight years younger, was much loved by Bamba. In later life, the young girl would recall how 'Princess Bamba retained her sense of humour, and as an old lady she would smile, wrinkle her nose, and giggle like a little girl' (Peter Bance, Sovereign, Squire and Rebel: Maharajah Duleep Singh, London 2009, p 160).
In 1953, Bamba decided to give Hampton House to the Crowes as she planned to return to Lahore (she had visited Punjab's capital in 1941 but was forced to remain there for five years following the outbreak of the Second World War). She died in her family's ancestral home in 1957. According to Oriel Crowe's (later Sutherland) letter of provenance accompanying this lot, Princess Sophia gifted the armlet to Mrs Ivy Janet, who later gave it to her. A forehead ornament with the same provenance was sold at Bonhams, Islamic and Indian Art, 11 June 2020, lot 230.







.jpg)
.jpg?w=400)





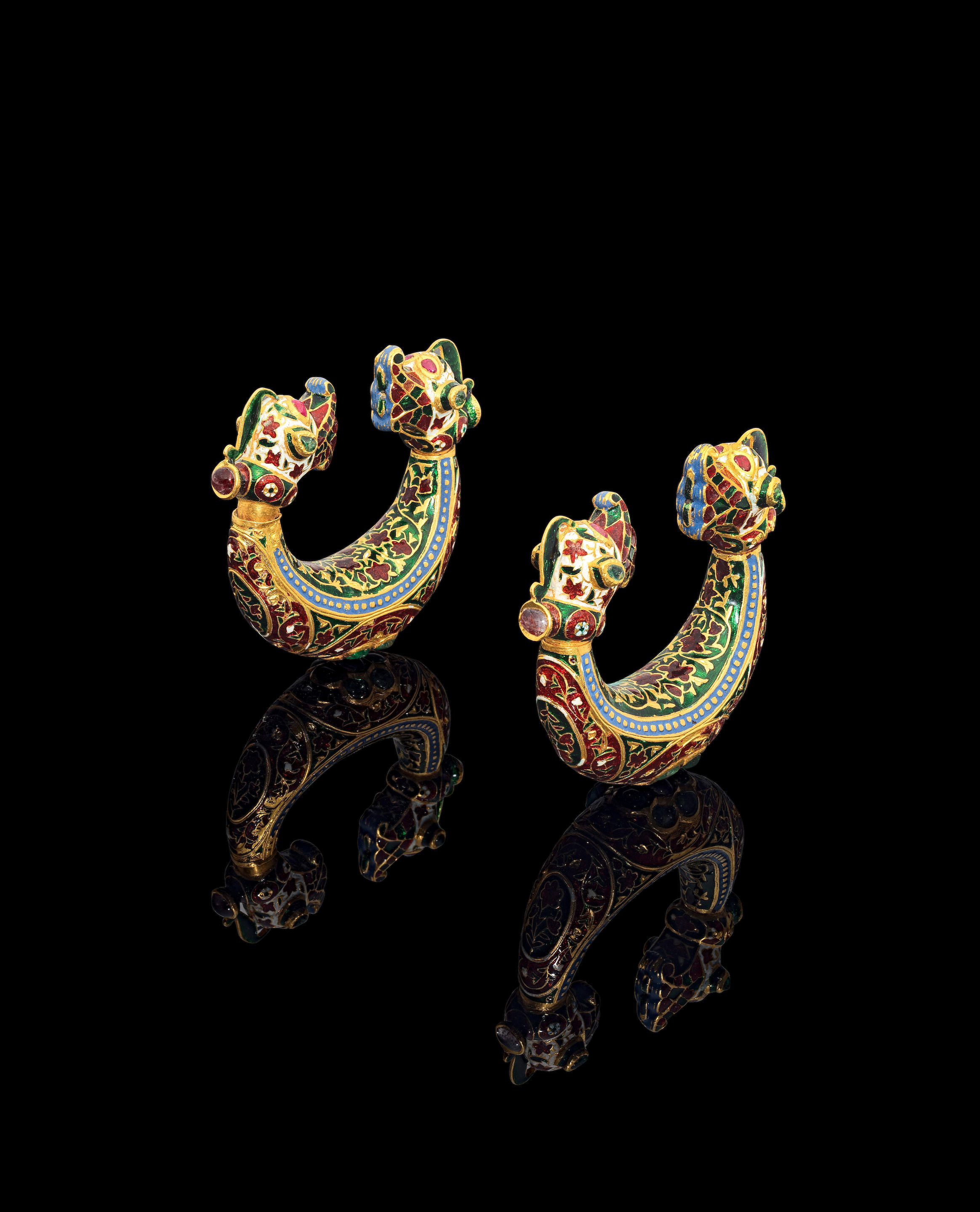
Testen Sie LotSearch und seine Premium-Features 7 Tage - ohne Kosten!
Lassen Sie sich automatisch über neue Objekte in kommenden Auktionen benachrichtigen.
Suchauftrag anlegen